Regional land and soil issues
The Waikato region can be divided into distinct topographical areas, each with their own resource management issues associated with land and soil.
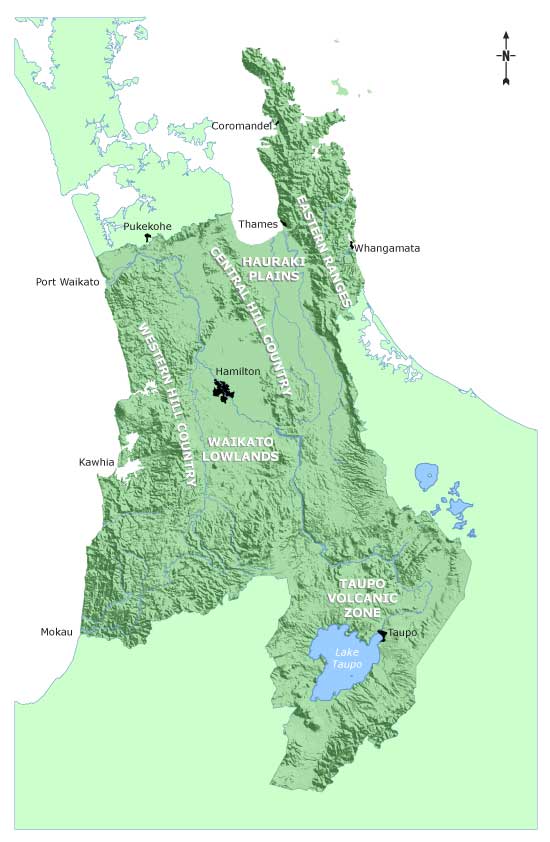
| Features | Land and soil issues | |
| Eastern Ranges | Volcanic in origin. Good quality soils in low lying areas. Land uses are dairy farming and horticulture (low lands), drystock farming, exotic forestry and native forest. |
Erosion where ranges cleared for pastoral farming or forestry. Soil quality. River bank erosion. Biodiversity – native forest and threatened species. |
| Waikato Lowlands and Hauraki Plains | Large areas of wetlands, peat soils and Hinuera formation. Flat land and gently rolling land. Approximately 80 percent of the Region's highly versatile soils are in this area. Land uses are urban and rural settlement, dairy farming, horticulture and cropping. |
Drainage and flood management. Erosion of Hinuera formation. Soil contamination. Soil quality. River bank erosion. Biodiversity – wetlands and native forest. |
| Western and Central Hill Country | Steep, sedimentary hill country, large tracts of native forest, extensive cave and karst systems. Land uses are extensive stock grazing and exotic forestry. |
Sheet and soil slip erosion of hill country. Soil quality. River bank erosion. Biodiversity – native forest. |
| Taupō Volcanic Zone | Pumice lands, high landscape values, geothermal features. Land uses are stock grazing, exotic forestry, dairy farming and native forest. |
Erosion of pumice soils. Soil quality. River bank erosion. Biodiversity – geothermal and alpine plants. |


